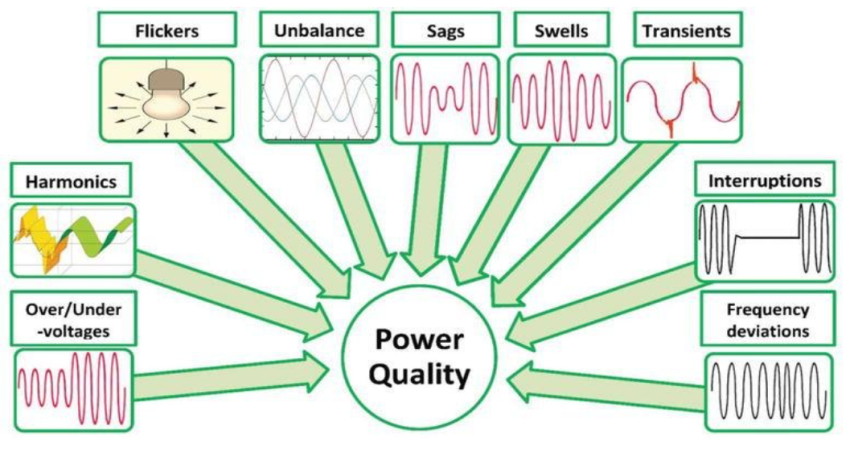
Power quality is a critical view of electrical engineering, playing a notable role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of electrical systems. In today’s technology-driven world, where industries and consumers depend on a stable power supply for everything from daily tasks to complex industrial processes, understanding the basic concept of power quality is essential. But what exactly does power quality mean, and why is it so important?
Defining Power Quality
At its core, power quality refers to the part of the electrical power provided to homes, businesses, and industries, and how well that power meets the demand of the equipment using it. The goal of good power quality is to supply a consistent, reliable, and stable voltage that confirms the safe and efficient operation of all electrical devices connected to the grid.
Key Elements of Power Quality
Several factors affect the quality of the electrical power supplied. To understand the basic concept of power quality, it’s necessary to look at the following components:
1. Voltage Consistency
Voltage levels should remain within an acceptable range for electrical devices to function properly. Any significant deviation from the standard voltage can cause problems. For instance, if the voltage drops too low (a voltage sag), equipment may not get enough power to operate. On the contrary, if the voltage surges too high (a voltage swell), it can damage sensitive electronics. Maintaining a consistent voltage is one of the primary objectives of power quality management.
2. Frequency Stability
Most electrical systems operate at a standard frequency, typically 50 Hz or 60 Hz depending on the region. The frequency must remain stable, as any fluctuation can influence the performance of motors, clocks, and other frequency-sensitive equipment. For example, deviations in frequency could lead to inefficient operation of industrial machinery or affect the accuracy of timekeeping devices.
3. Harmonics
Harmonics refer to distortions in the electrical waveform caused by non-linear loads like computers, LED lighting, and industrial machines. These distortions can impact the efficiency of the power system and cause overheating or equipment failure. Harmonic distortion is a growing concern as more electronic devices are connected to the grid. Making it a significant aspect of maintaining good power quality.
4. Power Factor
The power factor measures how effectively uses the electrical power. Ideally, the power factor should be as close to 1 as possible, meaning that most of the power is used for productive work rather than being wasted. A poor power factor can enhance energy consumption and put unnecessary strain on the electrical system, leading to higher costs and potential outages. Developing the power factor is a necessary outlook of power quality.
5. Transient Overvoltages
Transient overvoltages are short, sharp spikes in voltage that can occur because of events like lightning strikes or sudden switching of large electrical loads. These spikes can damage sensitive equipment and minimise the lifespan of electrical components. Surge protection devices used to mitigate the effects of transients and maintain good power quality.
The Importance of Power Quality
Power quality is not just a technical concept; it has real-world implications for businesses, consumers, and power utilities. Here are some reasons why maintaining good power quality is essential:
- Equipment Protection: Poor power quality can occur electrical equipment to malfunction or fail, leading to costly repairs or replacements. Sensitive devices like computers, medical equipment, and industrial machinery are particularly vulnerable to power disturbances.
- Energy Efficiency: Power quality impacts how efficiently uses the energy. For instance, a low power factor can lead to higher electricity bills. As more energy is needed to perform the same tasks. Improving power quality helps reduce energy consumption and lower operational costs.
- Reliability: Consistent and high-quality power confirms that industries, businesses, and households can operate without unexpected interruptions. Power outages or fluctuations can lead to downtime in factories, loss of data in computer systems, and discomfort in residential settings.
- Grid Stability: On a larger scale, maintaining good power quality is essential for the stability of the entire electrical grid. Poor power quality can lead to system imbalances, increased transmission losses, and even blackouts.
Conclusion
The basic concept of power quality revolves around delivering stable, consistent, and reliable electrical power to meet the demands of modern electrical devices and systems. By focusing on key elements like voltage consistency, frequency stability, harmonics, power factor, and protection from transient overvoltages, power quality ensures that equipment operates efficiently and without risk of damage. For businesses, industries, and households alike, understanding and maintaining power quality is crucial for reducing costs, protecting equipment, and ensuring the reliability of the electrical grid.
continue reading
Related Posts
Power Quality Disturbances are voltage sags, swells, spikes, fluctuation and […]
Maintaining Good Power Quality includes several important characteristics such as […]
Ensuring good power quality is crucial in electrical systems. As […]



